Cerebral Hypoxia: Forms And Causes
Cerebral hypoxia occurs when not enough oxygen reaches the brain. Find out more about the causes and dangers of this insufficient supply.

As cerebral hypoxia refers to an insufficient oxygen supply to the brain. It is a serious situation as the lack of oxygen can damage cells. If damage occurs, it can have far-reaching physical and mental consequences.
The brain needs large amounts of oxygen in order to guarantee its correct performance. Four large arteries supply the brain with oxygen-rich blood, but when the blood circulation is disturbed, the brain receives too little oxygen. After two minutes without oxygen, you usually pass out, after two to three minutes the first cells are damaged and after five minutes there is irreparable brain damage. A cerebral hypoxia has serious consequences!
Causes of cerebral hypoxia
There are many reasons for an insufficient supply of oxygen to the brain. For example, there may be circulatory disorders or an insufficient partial pressure of oxygen in the arterial blood.
For example, the following situations can lead to cerebral hypoxia:
- Altitude: When you are at high altitudes above sea level, your oxygen levels decrease. In this case we are talking about an “altitude sickness” from which mountaineers in particular suffer.
- Gas poisoning: Carbon monoxide is the main cause of this cause. In the case of gas poisoning, the oxygen in the blood is displaced by carbon monoxide. In this way, all cells of the body receive an element that they cannot use for their metabolism.
- Neurological diseases of the medullary brain: Some diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, attack the respiratory center of the brain by paralyzing the respiratory muscles. When the breathing mechanism fails, oxygen uptake is disturbed and a process similar to that of asphyxia occurs.
- Asphyxia: Both deliberate asphyxia due to criminal motives and accidental situations trigger cerebral hypoxia. Possible causes include choking, choking with liquids, or inhaling smoke in a fire.
- Hypotension: When blood pressure drops too low, it is no longer sufficient to supply all organs, especially those furthest from the heart. The brain is one of the most affected organs.
- Heart Problems: Any heart disease that restricts rhythmic pumping can cause cerebral hypoxia. It can be an acute event, such as a heart attack, or a chronic condition, such as an arrhythmia.
- Strokes: They cause cerebral hypoxia in certain areas, either because a cerebral artery is blocked by a blood clot or because part of the cerebral vessels burst and cause bleeding.
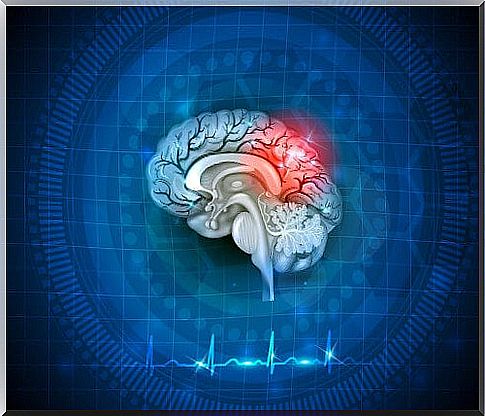
Forms of cerebral hypoxia
Depending on the brain area affected by the cerebral hypoxia, one speaks of different types. Some hypoxic seizures only injure cells in a specific area of the brain, while others stop all blood flow.
This is how one can describe the following types of cerebral hypoxia :
- Focal: The cerebral hypoxia in this case is limited to a specific location. The classic example is a stroke caused by a blood clot blocking an artery in the brain.
- Diffuse: This is the steady decrease in the flow of cerebral oxygen throughout the brain without causing serious effects. The functions of the brain cells decrease, but a heart attack rarely occurs.
- Global: Again, the reduction affects the entire brain, but it is serious. The lack of oxygen is significant and cells die. The consequences depend on which part of the brain is affected.
- Massive: It is a very serious situation in which large parts of the brain suffer from a heart attack at the same time, which is life-threatening and makes recovery difficult.
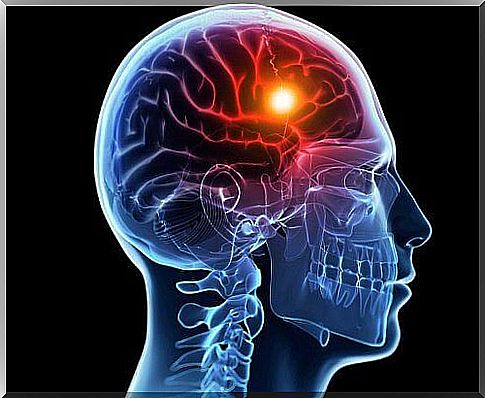
How can you tell if you have cerebral hypoxia?
Although symptoms of cerebral hypoxia depend on how long the lack of oxygen lasts, there are distinct characteristics. Note that hypoxia for a few seconds may not have any consequences. However, if it lasts for five minutes, a brain attack is likely to occur.
Momentary cerebral hypoxia can lead to poor concentration, memory loss, unusual feelings in the extremities of the body, speech disorders, etc. Movement restrictions are also possible.
A prolonged lack of oxygen supply leads to cramps, fainting with loss of consciousness or even a coma. In this case, it is a medical emergency that requires immediate life support.
If the five minutes of cerebral hypoxia are exceeded, a heart attack occurs. Recovery through rehabilitation is possible after a small heart attack, but a massive heart attack can result in death of the entire brain.
Therefore , you should definitely consult a specialist if you have any neurological symptoms. If a person passes out and does not respond immediately or has convulsions, it is best to call emergency services for quick help.